Abstract
Background: Clonal Hematopoiesis (CH) is associated with increased risk of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) (Desai et al, 2018). CH is also known to be pro-inflammatory and cells harboring CH mutations demonstrate a growth advantage under pro-inflammatory conditions. Thus, understanding the impact of pro inflammatory cytokines on progression from CH to AML is of potential prognostic and therapeutic importance.
Methods: Cytokine assays were performed on plasma from AML cases with baseline CH and matched controls collected as part of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI), a prospective cohort of healthy women aged 50-79 monitored for average 10.8 years.
The LEGENDplex human inflammation panel (BioLegend) (IL-1b, IL-18, IL6,TNF-a, IFN-a, IFN- γ, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12-P70, IL-17A, IL-23, IL-33) was run using a LSR II Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences) equipped with an HTS device to enable high throughput assessment in 96-well plate format. The bead-based assay used a combination of two bead sizes that could be distinguished by forward/side scatter and multiple intensities in APC channel, with each intensity corresponding to a particular inflammation marker. The panel was run in triplicate measurements per sample, with normalization to reference standards.
Statistical Analysis: Associations between each inflammatory marker and specific mutations, VAF, and clonal complexity were assessed using Pearson's Chi-squared test and Fisher's exact test. Association between cytokine levels and CH status was assessed using logistic regression adjusting for age and BMI, and between inflammatory factors and AML using a multivariable logistic regression model (covariables WHI treatment arm, CH, history of cancer, BMI, age and chemokine/cytokine; outcome variable AML case vs control).
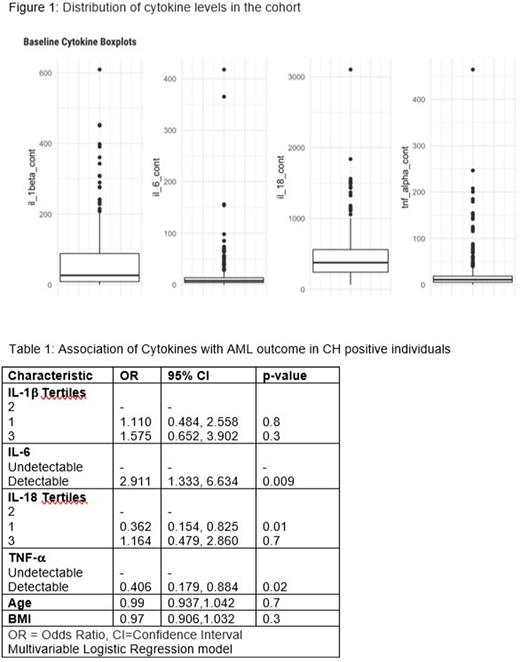
Results: We analyzed 126 AML cases and 133 unaffected controls (Fig 1). Cytokine levels were categorized into either tertiles (IL-1b, IL-18, and MCP-1) or as detectable/undetectable (UD) for IL-6, TNF-a, IFN-a, IFN- γ, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12-P70, IL-17A, IL-23 and IL-33 (Figure 1). As expected, older age (OR: 1.04; 95% CI: 1.00-1.08; p=0.03) and BMI were associated with CH (OR: 1.06; 95% CI: 1.01-1.12; p=0.03). After adjusting for other cytokines, age, and BMI, only detectable TNF-a was associated with increased odds of CH (OR: 1.84; 95% CI: 1.00-3.44; p=0.05). Detectable TNF-a was also associated with TET2 mutations (59% vs. 40% detectable in TET2 mutated vs. not, p=0.03). Similarly, elevated IL18 levels were associated with JAK2 mutations (mutated vs. not: 78% vs. 32% 3rd tertile, 0 vs. 32% 2nd tertile, 22% vs. 36% 1st tertile, p=0.01) and a borderline significant association with IDH mutations (mutated vs. not: 40% vs. 32% 3rd tertile, 53% vs. 32% 2nd tertile, 6.7% vs. 36% 1st tertile, p=0.05). DNMT3A, spliceosome and TP53 mutations were not associated with any of the 4 cytokines. Neither clonal complexity nor VAF >10% were associated with elevated cytokine levels.
After adjusting for CH, age, cancer history, BMI, detectable IL-6 was associated with increased odds of progression to AML (IL-6: OR: 2.42; 95% CI: 1.17-5.15; p=0.01) and lower IL-18 levels had lower odds of AML (referent 2nd tertile, 1st tertile OR: 0.44, 95% CI: 0.20-0.96; p=0.04, 3rd tertile OR: 1.35, 95% CI: 0.61-3.05, p=0.5. Detectable TNF-a was associated with reduced odds of AML (OR:0. 44; 95% CI:0. 20-0.90; p=0.02). IL-1b was not associated with AML. Finally, we analyzed the role of cytokines in progression to AML in participants with CH only (Table 1). In participants with baseline CH, detectable IL-6 was associated with increased risk of AML (OR: 2.91; 95% CI: 1.33-6.63; p=0.009) and lower IL-18 levels had lower odds of AML (referent 2nd tertile, 1st tertile OR: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.15-0.82; p=0.01, 3rd tertile OR: 1.16, 95% CI: 0.47-2.86, p=0.7). IL-1b was not associated with AML. Interestingly, detectable TNF-a was associated with reduced odds of AML (OR:0.40; 95% CI:0.17-0.88; p=0.02) compared to UD. Time to AML and serial sample analyses are pending and will available at the time of presentation.
Conclusions: In women with CH, detectable IL6 was associated with increased odds of progression to AML while lower IL18 levels were associated with lower risk. TNF-a was associated with TET2; IL-18 with JAK 2 and with IDH mutations, while VAF and clonal complexity were not associated with cytokine levels. Measurement of cytokines may be instrumental in risk stratification of patients with CH.
Disclosures
Desai:Janssen Research: Research Funding; Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Agios: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ritchie:Novartis: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy. Roboz:Bayer: Consultancy, Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Eisai: Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Jazz: Consultancy, Other: travel; Jasper Therapeutics: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Travel and accommodation expenses, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Onconova Therapeutics: Research Funding; Tensha Therapeutics: Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Other: travel; Agios: Other: travel, Research Funding; Mofitt Cancer Center: Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: Travel and Accommodation expenses, Research Funding; MedImmune: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals: Other: Travel and accommodation expenses, Research Funding; CTI: Research Funding; Celltrion: Consultancy, Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Clovis Oncology: Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Array BioPharma: Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Amphivena Therapeutics: Other: Travel and accommodation expenses, Research Funding; Mesoblast: Consultancy; Helsinn Therapeutics: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Otsuka: Consultancy; MEI Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Sandoz: Consultancy, Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Other: Travel and accommodation expenses; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: travel and accommodation expenses, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Other: travel and accommodation expenses, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: travel and accommodations, Research Funding; Actinium: Consultancy. Guzman:BridgeMedicines: Research Funding; Samus Therapeutics: Other: Inventor on licensed IP; Seq RX: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal